Why Do LED Lights Get Dim Over Time? 3 Common Causes Explained
Why Do LED Lights Get Dim Over Time? Three Common Reasons Explained
Many users notice that after a period of use, their LED lights are no longer as bright as they used to be.
The light still works, but the brightness has clearly dropped.
This is a common issue with LED lighting and does not always mean the light is defective. In most cases, LED lights get dim over time due to one or more of the following three reasons.
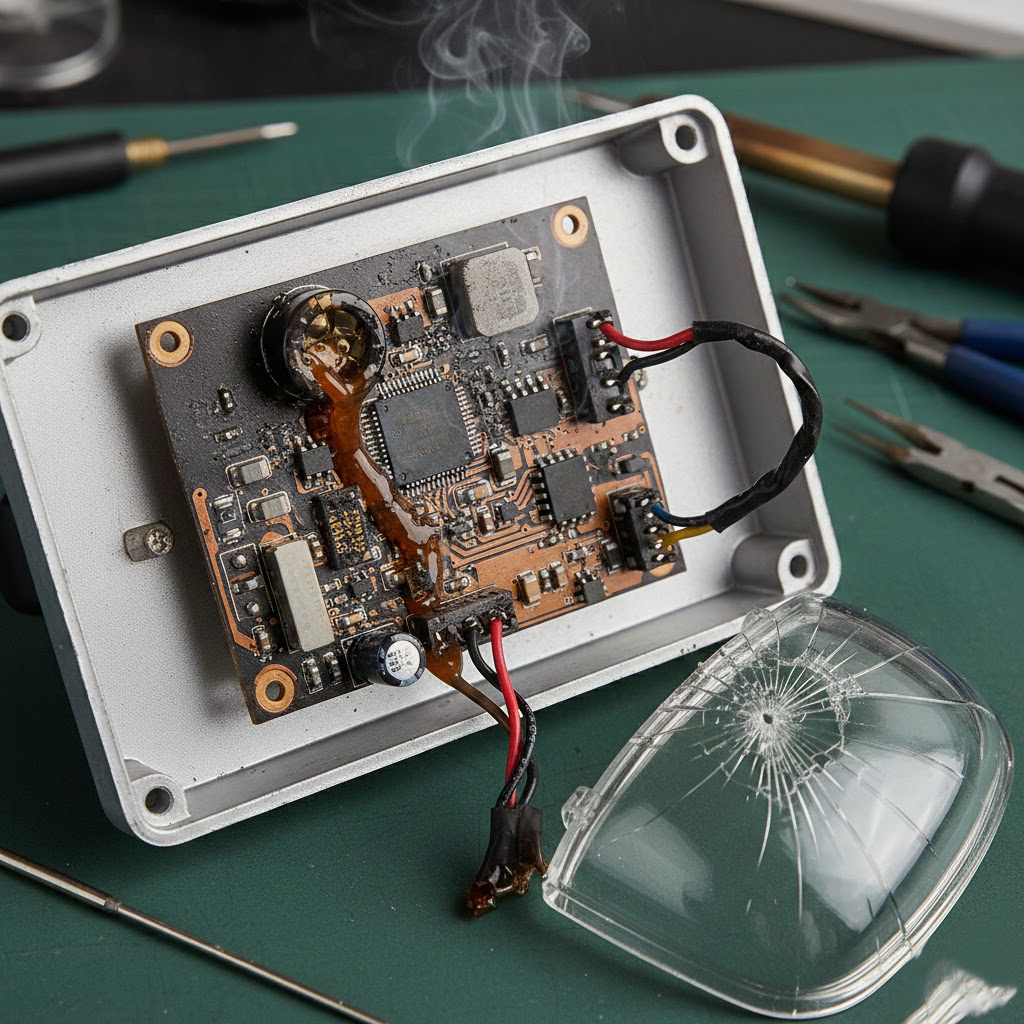
1. LED Driver Failure or Performance Degradation
The LED driver plays a critical role in any LED lighting system. Its main function is to convert incoming power into a stable voltage and current suitable for the LED chips.
What can go wrong?
-
Long-term exposure to high temperatures
-
Aging electronic components
-
Power surges or unstable input voltage
-
Low-quality driver design or materials
When the driver can no longer supply the correct current, the LED light may still turn on, but its brightness will be noticeably reduced. In some cases, users may also experience flickering or unstable light output.
How to reduce this risk:
-
Use high-quality LED drivers with over-voltage and over-temperature protection
-
Ensure the driver power rating matches the LED load
-
Avoid operating LED lights in excessively hot or humid environments

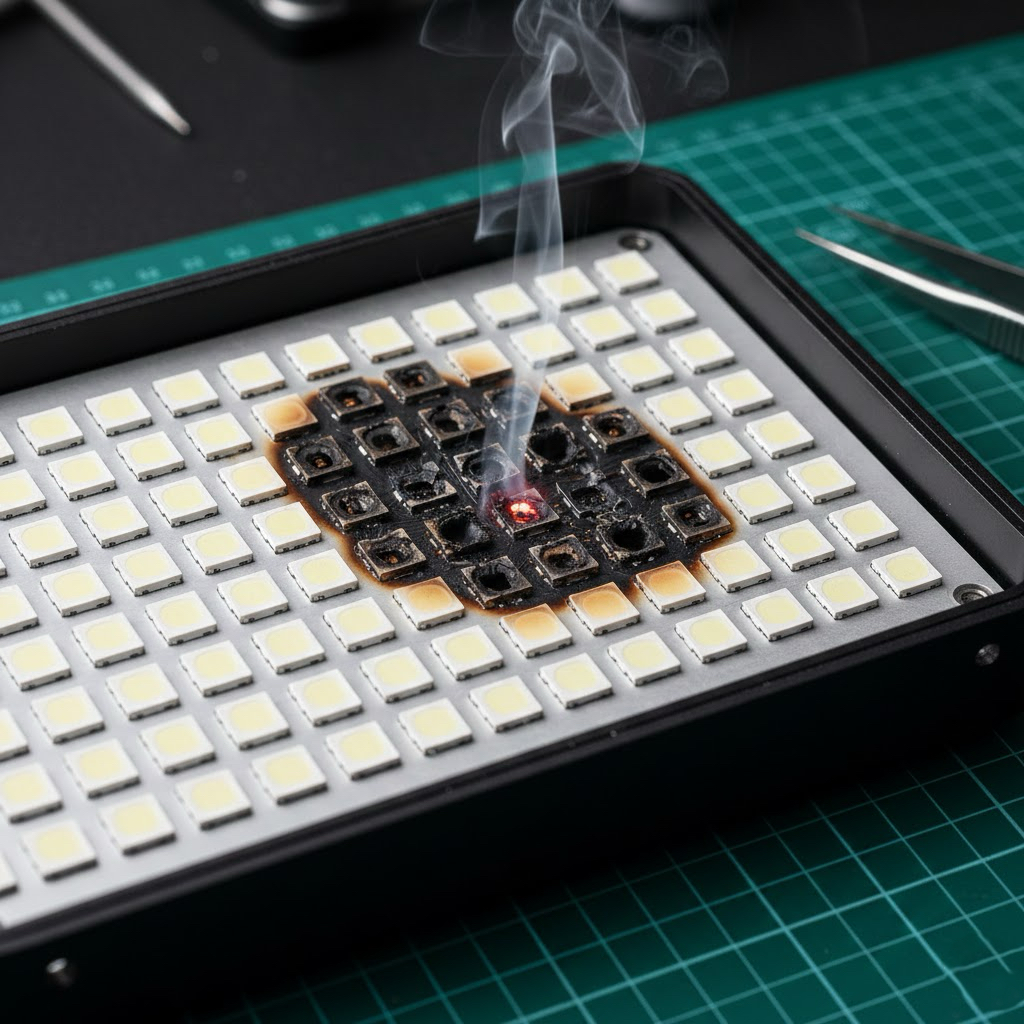
2. Partial LED Chip Damage or Burnout
LED lights usually contain multiple LED chips connected in series or parallel. Even if the light is still working, damage to some of the LED chips can reduce overall brightness.
Common causes include:
-
Overcurrent operation
-
Poor heat dissipation
-
Long-term thermal stress
Typical symptoms:
-
The light appears dimmer than before
-
Uneven brightness or dark spots
-
Reduced luminous efficiency
How to prevent LED chip damage:
-
Choose LED lights with high-quality, high-efficiency LED chips
-
Ensure proper thermal management and heat sink design
-
Avoid driving LEDs at excessive current levels

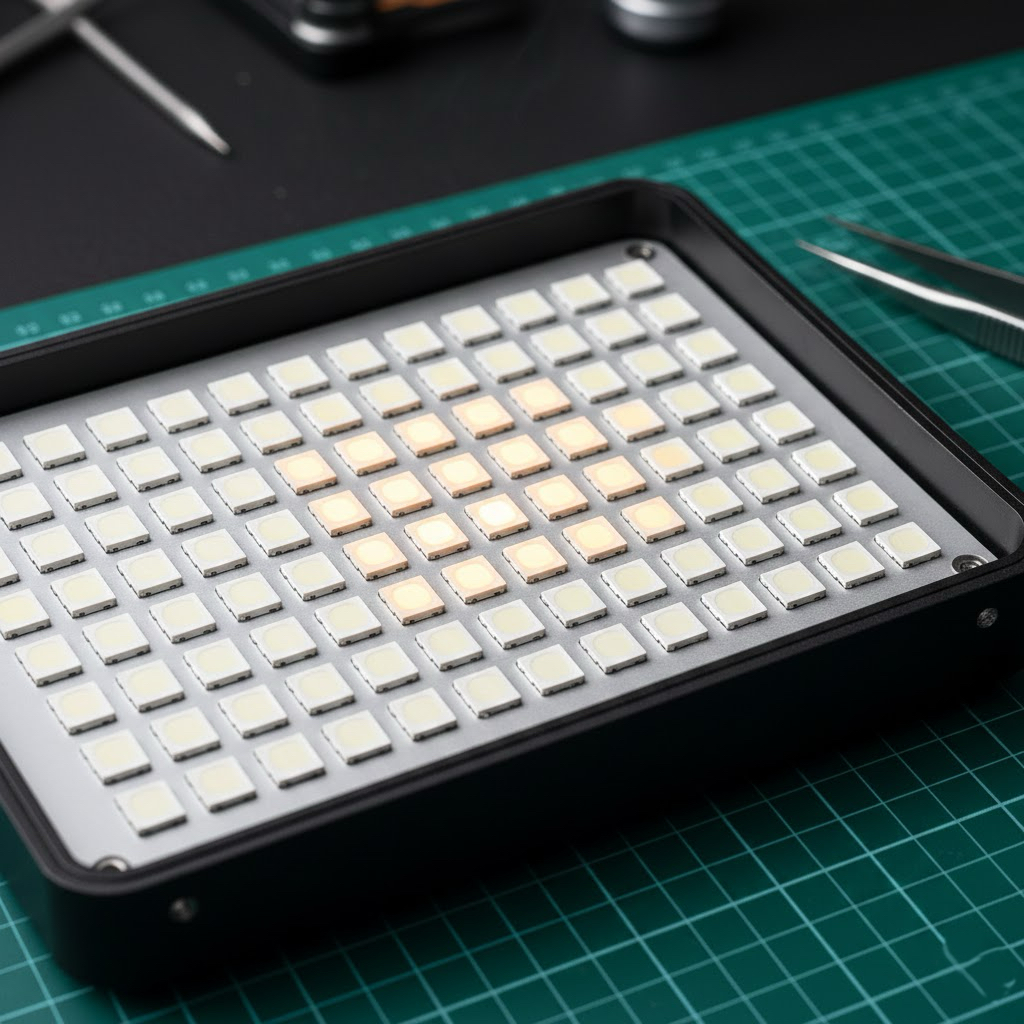
3. LED Lumen Depreciation (Light Degradation)
Lumen depreciation, also known as LED light decay, is the most common and unavoidable reason LED lights become dimmer over time.
What is LED lumen depreciation?
It refers to the gradual reduction in light output as LED chips age, even when they are still functioning normally.
Factors that accelerate lumen depreciation:
-
Continuous operation at high temperatures
-
Inadequate heat dissipation
-
Low-quality LED materials or packaging
High-quality LED products are typically rated to maintain:
-
About 70–80% of their original brightness after 10,000–30,000 hours of use
This means the light has not failed—it has simply aged.
How to slow down lumen depreciation:
-
Select LEDs with low lumen depreciation ratings
-
Use fixtures with efficient thermal design
-
Avoid long-term operation at maximum power in enclosed spaces

How to Extend the Lifespan of LED Lights
To keep LED lights bright and reliable for as long as possible, consider the following factors:
-
High-quality LED chips
-
Stable and efficient LED drivers
-
Proper heat dissipation design
-
Suitable operating environment
Focusing on these elements is often more important than simply choosing higher wattage or lower price products.
Conclusion
If your LED lights are getting dim over time, it does not necessarily indicate a product failure. In most cases, the causes can be traced to:
-
LED driver degradation
-
Partial LED chip damage
-
Natural LED lumen depreciation
Understanding these factors helps you make better decisions when selecting LED lighting products and ensures longer-lasting, more consistent performance.